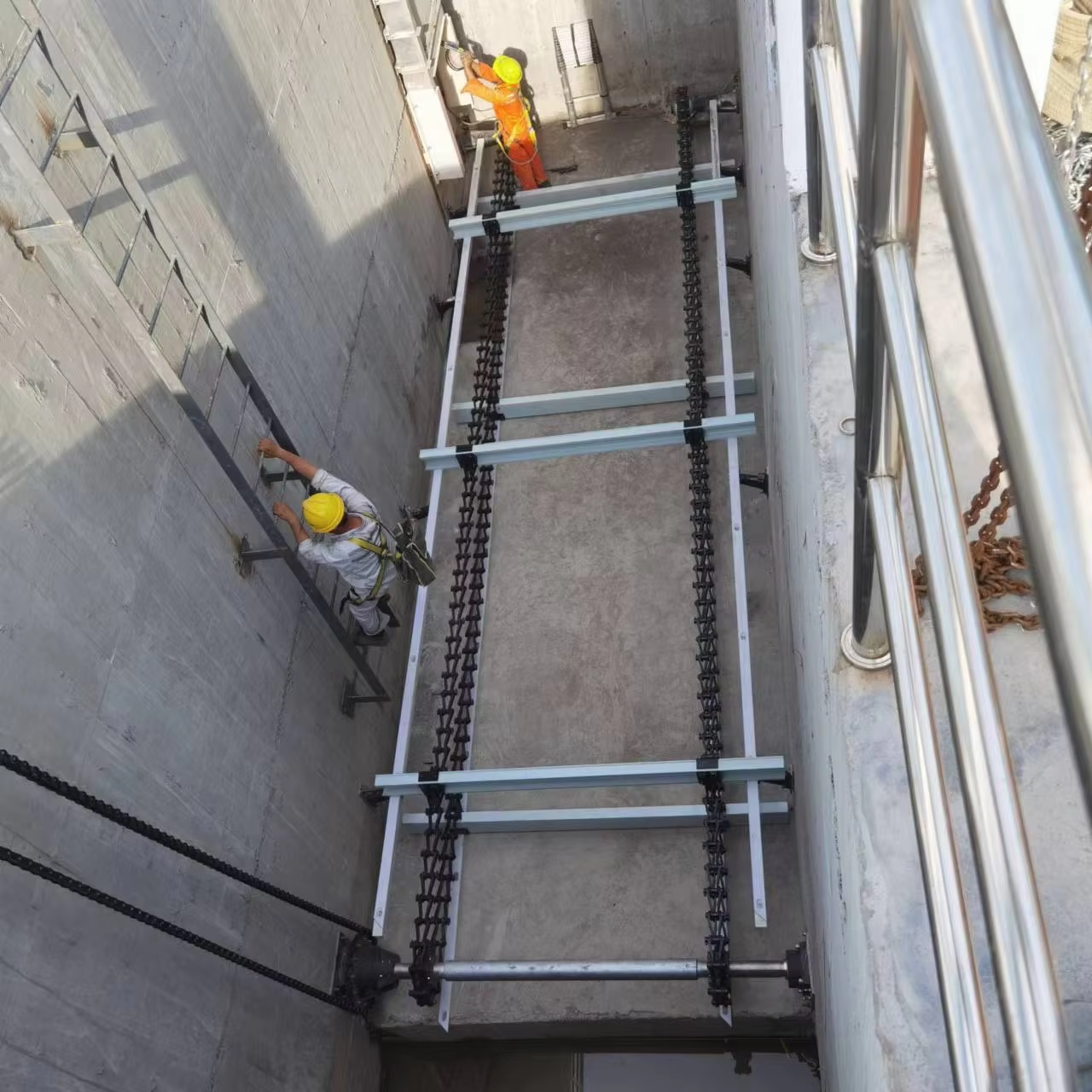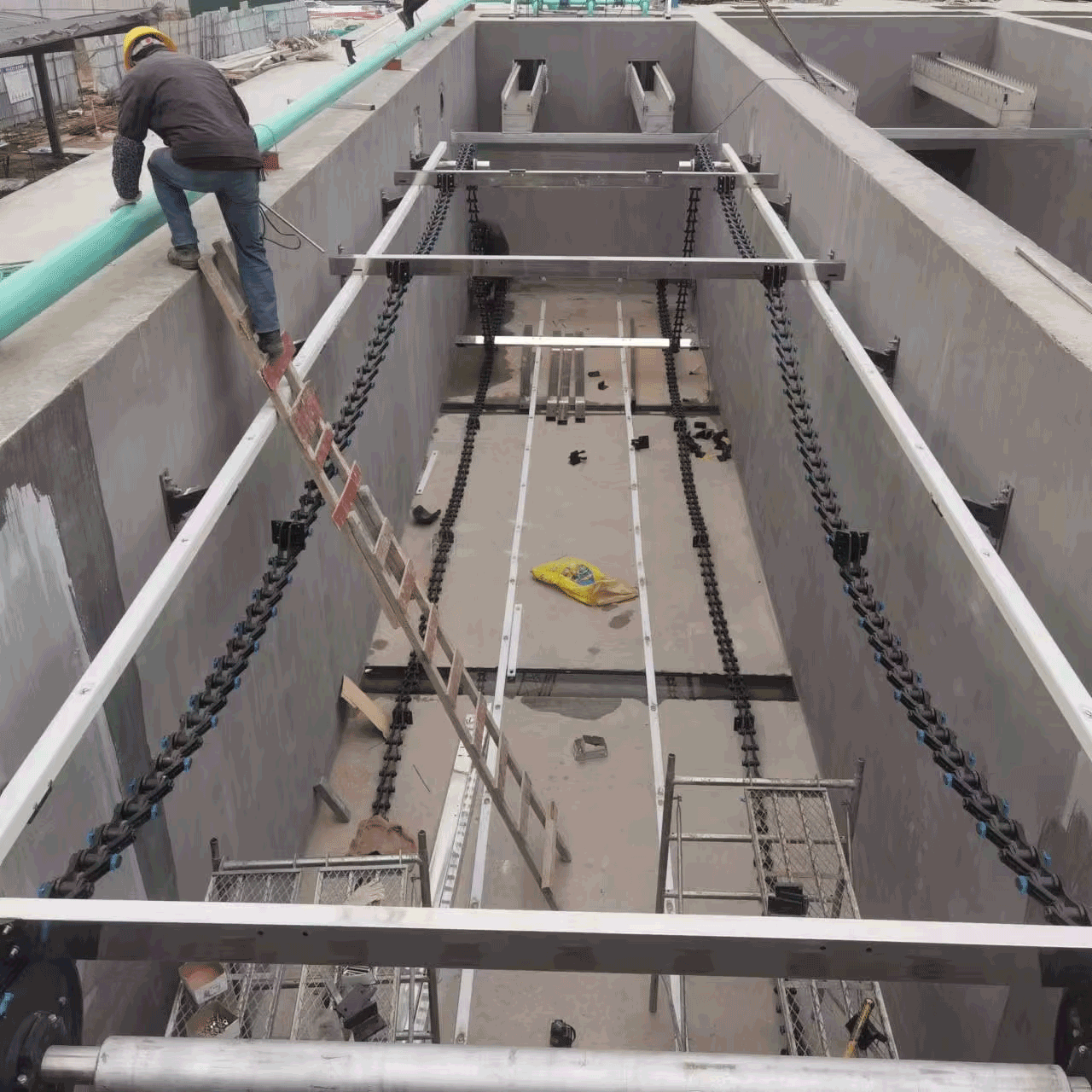
The phrase \"drainage treatment plant\" is commonly used to describe facilities which manage surface water runoff, referred to as stormwater, or a mix of both stormwater and wastewater. Unlike conventional sewage treatment plants in which the primary influent is domestic and industrial sewage, drainage treatment plants have to deal with highly variable inflow rates and contaminant loads as a result of rainstorms. The plant has to be equipped with the necessary infrastructure and machinery to withstand and deal with the sudden inflow of water and debris. Processes serve to treat water by removing pollutants such as suspended solids, hydrocarbons, heavy metals, and nutrients to the oil and water separator, filtration, and resonance. Before the water is released, there are water receiving bodies. Core components to this are sedimentation tanks or basins. Efficient collection of sludge is a necessary component of this. It is here where Huake Non-Metallic Sludge Scrapers operate. These scrapers are of exceptional quality and corrosion resistance. They are made to work in basins which may have extreme water level changes and have abrasive sediments and corrosive materials which come from roads and industrial areas. In the sludge areas and abrasive bottom sediments to scrape Huake scrapers operate efficiently. Supplying Huake scrapers to an industrial park drainage treatment facility illustrates this. The scrapers settle silt and contaminates. They do this after heavy rains and work to stop material buildup which can block the tank and slow the treatment.This guarantees that the facility does not exceed its environmental discharge parameters, safeguards regional water bodies from contamination, and necess almost constant case management, notwithstanding the difficult and variable conditions of the inflow.
